Heel Pain
Overview

Heel pain is one of the most common conditions to affect the foot. It is usually felt as an intense pain when the affected heel is used. The pain is usually worse when you get out of bed in the morning or after a long period of activity. In most cases, only one heel is affected. After walking, the pain usually improves. However, it is common for it to be painful when you first take a step after a period of rest. The pain often worsens by the end of the day. Most cases of Heel Pain are caused by damage and thickening of the plantar fascia. Sometimes, the surrounding tissue and the heel bone also become inflamed (swollen).
Causes
While heel pain has many causes, it is usually the result of faulty biomechanics (abnormalities in the way we walk). This can place too much stress on the heel bone and the soft tissues attached to it. The stress may also result from injury, or a bruise incurred while walking, running or jumping on hard surfaces; wearing poorly constructed footwear; or being significantly overweight. Systemic diseases such as arthritis and diabetes can also contribute to heel pain. A common cause of heel pain is the heel spur, a bony growth under the heel bone. There are no visible features on the heel, but a deep painful spot can be found in or around the middle of the sole of the heel (see diagram). Approximately 10 per cent of the population may have heel spurs without any pain. Heel spurs result from strain on the muscles of the foot. This may result from biomechanical imbalance, a condition occurring in many people. Both heel pain and heel spurs are frequently associated with an inflammation of the long band of tissue that connects the heel and the ball of the foot. The inflammation of this arch area is called plantar fasciitis. The inflammation may be aggravated by shoes that lack appropriate support, especially in the arch area, and by the chronic irritation that sometimes accompanies an athletic lifestyle.Excessive rolling in of the feet when walking. An inflamed bursa (bursitis), a small, irritated sack of fluid at the back of the heel. A neuroma (a nerve growth). Other soft-tissue growths. Heel bumps or ?pump bumps?, a bone enlargement at the back of the heel bone. Bruises or stress fractures to the heel bone.
Symptoms
Pain in the bottom of the heel is the most common symptom. The pain is often described as a knife-like, pinpoint pain that is worse in the morning and generally improves throughout the day. By the end of the day the pain may be replaced by a dull ache that improves with rest. The pain results from stretching the damaged tissues. For the same reason atheletes' pain occurs during beginning stages of exercise and is relieved over time as warm-up loosens the fascia. Plantar fasciitis onset is usually gradual, only flaring up during exercise. If pain is ignored, it can eventually interfere with walking and overall, plantar fasciitis accounts for about ten percent of all running injuries.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist (doctor who specializes in the evaluation and treatment of foot diseases) will carry out a physical examination, and ask pertinent questions about the pain. The doctor will also ask the patient how much walking and standing the patient does, what type of footwear is worn, and details of the his/her medical history. Often this is enough to make a diagnosis. Sometimes further diagnostic tests are needed, such as blood tests and imaging scans.
Non Surgical Treatment
The proper treatment for your heel pain depends entirely on the specific cause(s) of your symptoms. Therefore, it is critical to understand the cause(s) of your symptoms before beginning any treatment program and if you are unsure, then seeking medical advice is essential to develop the proper treatment program for your condition. Some common treatments are listed and can be performed at home. Keep in mind that not all of these treatments are appropriate for every condition, but they usually a good place to start. Rest, reducing activities for a few days can help to reduce the most severe pain. Ice, applying ice to the heel for 10 minutes several times a day will help to reduce inflammation. Stretching exercises, to lengthen the muscles in the back of the leg, including the hamstrings, will help to ease pain, reduce focal pressures to your feet and assist in recovery. For plantar fasciitis, this may be the best treatment of all. Avoid going barefoot, when without shoes excessive stress and strain is placed on the plantar fascia. Proper shoe gear, supportive shoes that fit and are not too worn along with good arch support help to reduce the stress and strain on the plantar fascia over time. Medications, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication, such as Motrin (ibuprofen), may help to reduce inflammation. If the pain persists or worsens after a couple of days, an appointment may be necessary where Dr. Talarico may add one or more of these additional modalities to your treatment program. Orthotic b, whether pre-fabricated or custom orthotic is used, these devices can help reduce the underlying structural abnormalities of the foot which have lead to the development of plantar fasciitis. These are often used to limit the recurrence of plantar fasciitis pain. Strapping, a special taping technique to help reduce the strain on the fascia. Injection therapy, in some instances injections are used to reduce the inflammation and reduce pain. Night Splint, this allows you to maintain an extended stretch on the plantar fascia while sleeping. Over time, this has shown to reduce the morning pain which some people experience. Removable Walking Cast, in some case of severe heel pain this may be used to keep your foot immobile for a few weeks allowing it to rest and heal. Physical Therapy may be recommended to aid in pain relief. At The Foot & Ankle Center, PC, Dr Talarico will often utilize two additional in-office modalities, EPAT and MLS Laser Therapy, which are very effective in treating most inflammatory conditions of the foot and ankle, including plantar fasciitis.
Surgical Treatment
Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require surgery. If required, surgery is usually for the removal of a spur, but also may involve release of the plantar fascia, removal of a bursa, or a removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
Prevention

You should always wear footwear that is appropriate for your environment and day-to-day activities. Wearing high heels when you go out in the evening is unlikely to be harmful. However, wearing them all week at work may damage your feet, particularly if your job involves a lot of walking or standing. Ideally, you should wear shoes with laces and a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels. Do not walk barefoot on hard ground, particularly while on holiday. Many cases of heel pain occur when a person protects their feet for 50 weeks of the year and then suddenly walks barefoot while on holiday. Their feet are not accustomed to the extra pressure, which causes heel pain. If you do a physical activity, such as running or another form of exercise that places additional strain on your feet, you should replace your sports shoes regularly. Most experts recommend that sports shoes should be replaced after you have done about 500 miles in them. It is also a good idea to always stretch after exercising, and to make strength and flexibility training a part of your regular exercise routine.

Heel pain is one of the most common conditions to affect the foot. It is usually felt as an intense pain when the affected heel is used. The pain is usually worse when you get out of bed in the morning or after a long period of activity. In most cases, only one heel is affected. After walking, the pain usually improves. However, it is common for it to be painful when you first take a step after a period of rest. The pain often worsens by the end of the day. Most cases of Heel Pain are caused by damage and thickening of the plantar fascia. Sometimes, the surrounding tissue and the heel bone also become inflamed (swollen).
Causes
While heel pain has many causes, it is usually the result of faulty biomechanics (abnormalities in the way we walk). This can place too much stress on the heel bone and the soft tissues attached to it. The stress may also result from injury, or a bruise incurred while walking, running or jumping on hard surfaces; wearing poorly constructed footwear; or being significantly overweight. Systemic diseases such as arthritis and diabetes can also contribute to heel pain. A common cause of heel pain is the heel spur, a bony growth under the heel bone. There are no visible features on the heel, but a deep painful spot can be found in or around the middle of the sole of the heel (see diagram). Approximately 10 per cent of the population may have heel spurs without any pain. Heel spurs result from strain on the muscles of the foot. This may result from biomechanical imbalance, a condition occurring in many people. Both heel pain and heel spurs are frequently associated with an inflammation of the long band of tissue that connects the heel and the ball of the foot. The inflammation of this arch area is called plantar fasciitis. The inflammation may be aggravated by shoes that lack appropriate support, especially in the arch area, and by the chronic irritation that sometimes accompanies an athletic lifestyle.Excessive rolling in of the feet when walking. An inflamed bursa (bursitis), a small, irritated sack of fluid at the back of the heel. A neuroma (a nerve growth). Other soft-tissue growths. Heel bumps or ?pump bumps?, a bone enlargement at the back of the heel bone. Bruises or stress fractures to the heel bone.
Symptoms
Pain in the bottom of the heel is the most common symptom. The pain is often described as a knife-like, pinpoint pain that is worse in the morning and generally improves throughout the day. By the end of the day the pain may be replaced by a dull ache that improves with rest. The pain results from stretching the damaged tissues. For the same reason atheletes' pain occurs during beginning stages of exercise and is relieved over time as warm-up loosens the fascia. Plantar fasciitis onset is usually gradual, only flaring up during exercise. If pain is ignored, it can eventually interfere with walking and overall, plantar fasciitis accounts for about ten percent of all running injuries.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist (doctor who specializes in the evaluation and treatment of foot diseases) will carry out a physical examination, and ask pertinent questions about the pain. The doctor will also ask the patient how much walking and standing the patient does, what type of footwear is worn, and details of the his/her medical history. Often this is enough to make a diagnosis. Sometimes further diagnostic tests are needed, such as blood tests and imaging scans.
Non Surgical Treatment
The proper treatment for your heel pain depends entirely on the specific cause(s) of your symptoms. Therefore, it is critical to understand the cause(s) of your symptoms before beginning any treatment program and if you are unsure, then seeking medical advice is essential to develop the proper treatment program for your condition. Some common treatments are listed and can be performed at home. Keep in mind that not all of these treatments are appropriate for every condition, but they usually a good place to start. Rest, reducing activities for a few days can help to reduce the most severe pain. Ice, applying ice to the heel for 10 minutes several times a day will help to reduce inflammation. Stretching exercises, to lengthen the muscles in the back of the leg, including the hamstrings, will help to ease pain, reduce focal pressures to your feet and assist in recovery. For plantar fasciitis, this may be the best treatment of all. Avoid going barefoot, when without shoes excessive stress and strain is placed on the plantar fascia. Proper shoe gear, supportive shoes that fit and are not too worn along with good arch support help to reduce the stress and strain on the plantar fascia over time. Medications, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication, such as Motrin (ibuprofen), may help to reduce inflammation. If the pain persists or worsens after a couple of days, an appointment may be necessary where Dr. Talarico may add one or more of these additional modalities to your treatment program. Orthotic b, whether pre-fabricated or custom orthotic is used, these devices can help reduce the underlying structural abnormalities of the foot which have lead to the development of plantar fasciitis. These are often used to limit the recurrence of plantar fasciitis pain. Strapping, a special taping technique to help reduce the strain on the fascia. Injection therapy, in some instances injections are used to reduce the inflammation and reduce pain. Night Splint, this allows you to maintain an extended stretch on the plantar fascia while sleeping. Over time, this has shown to reduce the morning pain which some people experience. Removable Walking Cast, in some case of severe heel pain this may be used to keep your foot immobile for a few weeks allowing it to rest and heal. Physical Therapy may be recommended to aid in pain relief. At The Foot & Ankle Center, PC, Dr Talarico will often utilize two additional in-office modalities, EPAT and MLS Laser Therapy, which are very effective in treating most inflammatory conditions of the foot and ankle, including plantar fasciitis.
Surgical Treatment
Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require surgery. If required, surgery is usually for the removal of a spur, but also may involve release of the plantar fascia, removal of a bursa, or a removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
Prevention

You should always wear footwear that is appropriate for your environment and day-to-day activities. Wearing high heels when you go out in the evening is unlikely to be harmful. However, wearing them all week at work may damage your feet, particularly if your job involves a lot of walking or standing. Ideally, you should wear shoes with laces and a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels. Do not walk barefoot on hard ground, particularly while on holiday. Many cases of heel pain occur when a person protects their feet for 50 weeks of the year and then suddenly walks barefoot while on holiday. Their feet are not accustomed to the extra pressure, which causes heel pain. If you do a physical activity, such as running or another form of exercise that places additional strain on your feet, you should replace your sports shoes regularly. Most experts recommend that sports shoes should be replaced after you have done about 500 miles in them. It is also a good idea to always stretch after exercising, and to make strength and flexibility training a part of your regular exercise routine.
Achilles Tendon Pain Cause And Treatment
Overview
 Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your calf muscles to your heel bone and is used when you walk, run, and jump. Although the Achilles tendon can withstand great stresses from running and jumping, it is also prone to tendonitis, a condition associated with overuse and degeneration. Tendons become inflamed for a variety of reasons, and the action of pulling the muscle becomes irritating. If the normal, smooth gliding motion of the tendon is impaired, the tendon will become inflamed and movement will become painful. This is called tendonitis, meaning inflammation of the tendon. Achilles tendonitis is typically not related to a specific injury. The problem results from repetitive stress to the tendon. This often happens when we push our bodies to do too much, too soon, but other factors can make it more likely to develop tendinitis, including: a sudden increase in the amount or intensity of exercise activity, tight calf muscles, or a bone spur that has developed where the tendon attaches to the heel bone.
Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your calf muscles to your heel bone and is used when you walk, run, and jump. Although the Achilles tendon can withstand great stresses from running and jumping, it is also prone to tendonitis, a condition associated with overuse and degeneration. Tendons become inflamed for a variety of reasons, and the action of pulling the muscle becomes irritating. If the normal, smooth gliding motion of the tendon is impaired, the tendon will become inflamed and movement will become painful. This is called tendonitis, meaning inflammation of the tendon. Achilles tendonitis is typically not related to a specific injury. The problem results from repetitive stress to the tendon. This often happens when we push our bodies to do too much, too soon, but other factors can make it more likely to develop tendinitis, including: a sudden increase in the amount or intensity of exercise activity, tight calf muscles, or a bone spur that has developed where the tendon attaches to the heel bone.
Causes
Achilles tendonitis is an overuse injury that is common especially to joggers and jumpers, due to the repetitive action and so may occur in other activities that requires the same repetitive action. Most tendon injuries are the result of gradual wear and tear to the tendon from overuse or ageing. Anyone can have a tendon injury, but people who make the same motions over and over in their jobs, sports, or daily activities are more likely to damage a tendon. A tendon injury can happen suddenly or little by little. You are more likely to have a sudden injury if the tendon has been weakened over time. Common causes of Achilles tendonitis include, over-training or unaccustomed use,?too much too soon?. Sudden change in training surface e.g. grass to bitumen. Flat (over-pronated) feet, High foot arch with tight Achilles tendon. tight hamstring (back of thigh) and calf muscles, toe walking (or constantly wearing high heels). Poorly supportive footwear, hill running. Poor eccentric strength.
Symptoms
If you have Achilles tendinitis or Achilles enthesopathy, you are likely to experience the following symptoms. Pain. You may notice aching, burning, or tearing pains at the back of your heel or above the ankle. The pain can range from mild to very severe and disabling. It is most noticeable in the following circumstances. After resting. Many people report that pain increases when they first get out of bed in the morning or after sitting for a period of time. After exercise. Pain may increase if you exercise or stand for a period of time. A lump. In some cases, a tender lump can develop at the site of the injured tendon (tendinosis). Bone spurs. When the injury occurs at the point where the tendon attaches to the foot, a bone spur may develop on the heel.
Diagnosis
When diagnosing Achilles tendinitis, a doctor will ask the patient a few questions about their symptoms and then perform a physical examination. To perform a physical exam on the Achilles tendon, the doctor will lightly touch around the back of the ankle and tendon to locate the source of the pain or inflammation. They will also test the foot and ankle to see if their range of motion and flexibility has been impaired. The doctor might also order an imaging test to be done on the tendon. This will aid in the elimination of other possible causes of pain and swelling, and may help the doctor assess the level of damage (if any) that has been done to the tendon. Types of imaging tests that could be used for diagnosing Achilles tendinitis are MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging), X-ray, Ultrasound.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Physical therapy is the first and most useful defense for achilles tendonitis because of the two presentations outlined above. Treatments for the two types are quite different in approach. Midsubstance tendinitis responds well to stretching, whereas insertional tendnitis tends to be aggravated more by it. Depend on your trusted physical therapist to differentiate between the two and follow their guidelines on exercises and running modifications. Running gait patterns that show excessive ?sinking postures? tend to point to the source of achilles tendon problems. Altering your gait in the midstance phase of the cycle can reduce the load on the tendon dramatically and thereby reduce pain. Rely on your running physical therapist for proper guidance on altering your gait the right way. Stride Strong?s Portland Running Clinic gait analysis can identify and fix potential issues before pain sets in. Icing at the onset of acute achilles pain (i.e. when the injury is fresh and new) would help control the inflammation. Your next step should be to call our number for an appointment.

Surgical Treatment
If several months of more-conservative treatments don't work or if the tendon has torn, your doctor may suggest surgery to repair your Achilles tendon.
Prevention
While it may not be possible to prevent Achilles tendinitis, you can take measures to reduce your risk. Increase your activity level gradually. If you're just beginning an exercise regimen, start slowly and gradually increase the duration and intensity of the training. Take it easy. Avoid activities that place excessive stress on your tendons, such as hill running. If you participate in a strenuous activity, warm up first by exercising at a slower pace. If you notice pain during a particular exercise, stop and rest. Choose your shoes carefully. The shoes you wear while exercising should provide adequate cushioning for your heel and should have a firm arch support to help reduce the tension in the Achilles tendon. Replace your worn-out shoes. If your shoes are in good condition but don't support your feet, try arch supports in both shoes. Stretch daily. Take the time to stretch your calf muscles and Achilles tendon in the morning, before exercise and after exercise to maintain flexibility. This is especially important to avoid a recurrence of Achilles tendinitis. Strengthen your calf muscles. Strong calf muscles enable the calf and Achilles tendon to better handle the stresses they encounter with activity and exercise. Cross-train. Alternate high-impact activities, such as running and jumping, with low-impact activities, such as cycling and swimming.
 Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your calf muscles to your heel bone and is used when you walk, run, and jump. Although the Achilles tendon can withstand great stresses from running and jumping, it is also prone to tendonitis, a condition associated with overuse and degeneration. Tendons become inflamed for a variety of reasons, and the action of pulling the muscle becomes irritating. If the normal, smooth gliding motion of the tendon is impaired, the tendon will become inflamed and movement will become painful. This is called tendonitis, meaning inflammation of the tendon. Achilles tendonitis is typically not related to a specific injury. The problem results from repetitive stress to the tendon. This often happens when we push our bodies to do too much, too soon, but other factors can make it more likely to develop tendinitis, including: a sudden increase in the amount or intensity of exercise activity, tight calf muscles, or a bone spur that has developed where the tendon attaches to the heel bone.
Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your calf muscles to your heel bone and is used when you walk, run, and jump. Although the Achilles tendon can withstand great stresses from running and jumping, it is also prone to tendonitis, a condition associated with overuse and degeneration. Tendons become inflamed for a variety of reasons, and the action of pulling the muscle becomes irritating. If the normal, smooth gliding motion of the tendon is impaired, the tendon will become inflamed and movement will become painful. This is called tendonitis, meaning inflammation of the tendon. Achilles tendonitis is typically not related to a specific injury. The problem results from repetitive stress to the tendon. This often happens when we push our bodies to do too much, too soon, but other factors can make it more likely to develop tendinitis, including: a sudden increase in the amount or intensity of exercise activity, tight calf muscles, or a bone spur that has developed where the tendon attaches to the heel bone.
Causes
Achilles tendonitis is an overuse injury that is common especially to joggers and jumpers, due to the repetitive action and so may occur in other activities that requires the same repetitive action. Most tendon injuries are the result of gradual wear and tear to the tendon from overuse or ageing. Anyone can have a tendon injury, but people who make the same motions over and over in their jobs, sports, or daily activities are more likely to damage a tendon. A tendon injury can happen suddenly or little by little. You are more likely to have a sudden injury if the tendon has been weakened over time. Common causes of Achilles tendonitis include, over-training or unaccustomed use,?too much too soon?. Sudden change in training surface e.g. grass to bitumen. Flat (over-pronated) feet, High foot arch with tight Achilles tendon. tight hamstring (back of thigh) and calf muscles, toe walking (or constantly wearing high heels). Poorly supportive footwear, hill running. Poor eccentric strength.
Symptoms
If you have Achilles tendinitis or Achilles enthesopathy, you are likely to experience the following symptoms. Pain. You may notice aching, burning, or tearing pains at the back of your heel or above the ankle. The pain can range from mild to very severe and disabling. It is most noticeable in the following circumstances. After resting. Many people report that pain increases when they first get out of bed in the morning or after sitting for a period of time. After exercise. Pain may increase if you exercise or stand for a period of time. A lump. In some cases, a tender lump can develop at the site of the injured tendon (tendinosis). Bone spurs. When the injury occurs at the point where the tendon attaches to the foot, a bone spur may develop on the heel.
Diagnosis
When diagnosing Achilles tendinitis, a doctor will ask the patient a few questions about their symptoms and then perform a physical examination. To perform a physical exam on the Achilles tendon, the doctor will lightly touch around the back of the ankle and tendon to locate the source of the pain or inflammation. They will also test the foot and ankle to see if their range of motion and flexibility has been impaired. The doctor might also order an imaging test to be done on the tendon. This will aid in the elimination of other possible causes of pain and swelling, and may help the doctor assess the level of damage (if any) that has been done to the tendon. Types of imaging tests that could be used for diagnosing Achilles tendinitis are MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging), X-ray, Ultrasound.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Physical therapy is the first and most useful defense for achilles tendonitis because of the two presentations outlined above. Treatments for the two types are quite different in approach. Midsubstance tendinitis responds well to stretching, whereas insertional tendnitis tends to be aggravated more by it. Depend on your trusted physical therapist to differentiate between the two and follow their guidelines on exercises and running modifications. Running gait patterns that show excessive ?sinking postures? tend to point to the source of achilles tendon problems. Altering your gait in the midstance phase of the cycle can reduce the load on the tendon dramatically and thereby reduce pain. Rely on your running physical therapist for proper guidance on altering your gait the right way. Stride Strong?s Portland Running Clinic gait analysis can identify and fix potential issues before pain sets in. Icing at the onset of acute achilles pain (i.e. when the injury is fresh and new) would help control the inflammation. Your next step should be to call our number for an appointment.

Surgical Treatment
If several months of more-conservative treatments don't work or if the tendon has torn, your doctor may suggest surgery to repair your Achilles tendon.
Prevention
While it may not be possible to prevent Achilles tendinitis, you can take measures to reduce your risk. Increase your activity level gradually. If you're just beginning an exercise regimen, start slowly and gradually increase the duration and intensity of the training. Take it easy. Avoid activities that place excessive stress on your tendons, such as hill running. If you participate in a strenuous activity, warm up first by exercising at a slower pace. If you notice pain during a particular exercise, stop and rest. Choose your shoes carefully. The shoes you wear while exercising should provide adequate cushioning for your heel and should have a firm arch support to help reduce the tension in the Achilles tendon. Replace your worn-out shoes. If your shoes are in good condition but don't support your feet, try arch supports in both shoes. Stretch daily. Take the time to stretch your calf muscles and Achilles tendon in the morning, before exercise and after exercise to maintain flexibility. This is especially important to avoid a recurrence of Achilles tendinitis. Strengthen your calf muscles. Strong calf muscles enable the calf and Achilles tendon to better handle the stresses they encounter with activity and exercise. Cross-train. Alternate high-impact activities, such as running and jumping, with low-impact activities, such as cycling and swimming.
What Triggers Pain At The Heel And How To Treat It

Overview
The plantar fascia is a ligament that connects the heel to the toes on the bottom of the foot. It lies just below the skin layers as it passes over the arch of the foot. A common ailment called plantar fasciitis is the result of this ligament becomes inflamed. This can Foot anatomyhappen from injury, physical stress, or sometimes for no obvious reason. The most common point for this inflammation is where this ligament joints the heel bone. Typical symptoms are the pain on the bottom of the foot near the heel usually most intense in the mornings when arising or after a long period with little movement. The pain typically diminishes with movement. Many suffering from plantar fasciitis have heel spurs. Even though they are in the same area they are unrelated and the heel spurs do not cause the plantar fasciitis. Most times heel spurs will not cause pain and in many go undetected unless they have an x-ray for some other reason.
Causes
Plantar Fasciitis is caused by abnormal pronation of the foot. Contributing factors are obesity, weight gain, jobs that require a lot of walking or standing on hard surfaces, badly worn shoes with little support, and also inactivity. As a result of over-pronation, with every step the Plantar Fascia (band of tissue under the foot) is being stretched, resulting in inflammation, irritation and pain at the attachment of the fascia into the heel bone. In some cases the pain is felt under the foot, in the arch. Continuous pulling of the fascia at the heel bone, eventually may lead to the development of bony growth on the heel. This is called a heel spur. When you’re at rest, such as while sleeping, the Plantar Fascia tightens and shortens. When body weight is rapidly applied to the foot, the Fascia must stretch and quickly lengthen, causing micro-tears in the Fascia. As a result, the foot pain is more severe with your first steps in the morning, or after sitting for a long period. Plantar Fasciitis is more likely to happen if you suffer from over-pronation (flattening of the arch), you stand or walk on hard surfaces, for long periods, you are overweight or pregnant, you have tight calf muscles.
Symptoms
The pain associated with plantar fasciitis is typically gradual in onset and is usually located over the inner or medial aspect of the heel. Occasionally, the pain will be sudden in onset, occurring after missing a step or after jumping from a height. The pain is commonly most severe upon arising from bed in the morning, or after periods of inactivity during the day. Thus, it causes what is known as "first-step pain." The degree of discomfort can sometimes lessen with activity during the course of the day or after "warming-up", but can become worse if prolonged or vigorous activity is undertaken. The pain is also often noted to be more severe in bare feet or in shoes with minimal or no padding at the sole.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will check your feet and watch you stand and walk. He or she will also ask questions about your past health, including what illnesses or injuries you have had. Your symptoms, such as where the pain is and what time of day your foot hurts most. How active you are and what types of physical activity you do. Your doctor may take an X-ray of your foot if he or she suspects a problem with the bones of your foot, such as a stress fracture.
Non Surgical Treatment
The key for the proper treatment of plantar fasciitis is determining what is causing the excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. When the cause is over-pronation (flat feet), an orthotic with rearfoot posting and longitudinal arch support is an effective device to reduce the over-pronation and allow the condition to heal. If you have usually high arches, which can also lead to plantar fasciitis, cushion the heel, absorb shock and wear proper footwear that will accommodate and comfort the foot. Other common treatments include stretching exercises, plantar fasciitis night splints, wearing shoes that have a cushioned heel to absorb shock, and elevating the heel with the use of a heel cradle or heel cup. Heel cradles and heel cups provide extra comfort, cushion the heel, and reduce the amount of shock and shear forces placed during everyday activities.
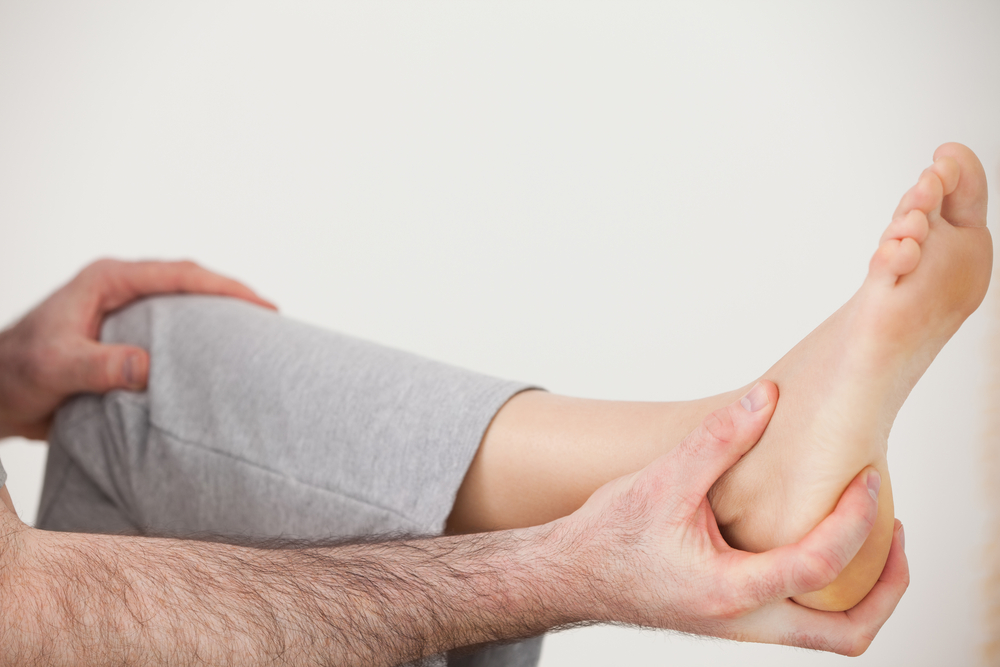

Surgical Treatment
Surgery should be reserved for patients who have made every effort to fully participate in conservative treatments, but continue to have pain from plantar fasciitis. Patients should fit the following criteria. Symptoms for at least 9 months of treatment. Participation in daily treatments (exercises, stretches, etc.). If you fit these criteria, then surgery may be an option in the treatment of your plantar fasciitis. Unfortunately, surgery for treatment of plantar fasciitis is not as predictable as a surgeon might like. For example, surgeons can reliably predict that patients with severe knee arthritis will do well after knee replacement surgery about 95% of the time. Those are very good results. Unfortunately, the same is not true of patients with plantar fasciitis.
Prevention
To reduce your risk of getting plantar fasciitis take these steps. Wear appropriate and well-fitted footwear during sports and exercise. Do stretching exercises for the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia. Increase the intensity and duration of exercise gradually. Maintain an appropriate weight.
What Is Plantar Fasciitis And How To Cure It

Overview
If your first few steps out of bed in the morning cause severe pain in the heel of your foot, you may have plantar fasciitis, an overuse injury that affects the sole of the foot. A diagnosis of plantar fasciitis means you have inflamed the tough, fibrous band of tissue (fascia) connecting your heel bone to the base of your toes.
Causes
You are at a greater risk for developing plantar fasciitis if you are overweight or obese. This is due to the increased pressure on your plantar fascia ligaments, especially if you have sudden weight gain. Women who are pregnant often experience bouts of plantar fasciitis, particularly during late pregnancy. If you are a long distance runner, you may be more likely to develop plantar fascia problems. You are also at risk if you have a very active job that involves being on your feet often, such as a factory worker or a restaurant server. Active men and women between the ages of 40 and 70 are at the highest risk for developing plantar fasciitis. It is also slightly more common in women than men. If you have foot problems, such as very high arches or very flat feet, you may develop plantar fasciitis. Tight Achilles tendons (the tendons attaching the calf muscles to the heels) may also result in plantar fascia pain. Simply wearing shoes with soft soles and poor arch support can also result in plantar fasciitis. Plantar fasciitis is not caused by heel spurs. A heel spur is a hook of bone that can form on the heel bone (calcaneus) of the foot. One out of every 10 people has a heel spur, but only one out of 20 people with heel spurs experience pain, according to OrthoInfo.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis is usually found in one foot. While bilateral plantar fasciitis is not unheard of, this condition is more the result of a systemic arthritic condition that is extremely rare in an athletic population. There is a greater incidence of plantar fasciitis in males than females (Ambrosius 1992). While no direct cause could be found it could be argued that males are generally heavier which, when combined with the greater speeds, increased ground contact forces, and less flexibility, may explain the greater injury predisposition. The most notable characteristic of plantar fasciitis is pain upon rising, particularly the first step out of bed. This morning pain can be located with pinpoint accuracy at the bony landmark on the anterior medial tubercle of the calcaneus. The pain may be severe enough to prevent the athlete from walking barefooted in a normal heel-toe gait. Other less common presentations include referred pain to the subtalar joint, the forefoot, the arch of the foot or the achilles tendon (Brantingham 1992). After several minutes of walking the pain usually subsides only to re turn with the vigorous activity of the day's training session. The problem should be obvious to the coach as the athlete will exhibit altered gait and/ or an abnormal stride pattern, and may complain of foot pain during running/jumping activities. Consistent with plantar fascia problems the athlete will have a shortened gastroc complex. This can be evidenced by poor dorsiflexion (lifting the forefoot off the ground) or inability to perform the "flying frog" position. In the flying frog the athlete goes into a full squat position and maintains balance and full ground contact with the sole of the foot. Elevation of the heel signifies a tight gastroc complex. This test can be done with the training shoes on.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will check your feet and watch you stand and walk. He or she will also ask questions about your past health, including what illnesses or injuries you have had. Your symptoms, such as where the pain is and what time of day your foot hurts most. How active you are and what types of physical activity you do. Your doctor may take an X-ray of your foot if he or she suspects a problem with the bones of your foot, such as a stress fracture.
Non Surgical Treatment
In general, plantar fasciitis is a self-limiting condition. Unfortunately, the time until resolution is often six to 18 months, which can lead to frustration for patients and physicians. Rest was cited by 25 percent of patients with plantar fasciitis in one study as the treatment that worked best. Athletes, active adults and persons whose occupations require lots of walking may not be compliant if instructed to stop all activity. Many sports medicine physicians have found that outlining a plan of “relative rest” that substitutes alternative forms of activity for activities that aggravate the symptoms will increase the chance of compliance with the treatment plan. It is equally important to correct the problems that place individuals at risk for plantar fasciitis, such as increased amount of weight-bearing activity, increased intensity of activity, hard walking/running surfaces and worn shoes. Early recognition and treatment usually lead to a shorter course of treatment as well as increased probability of success with conservative treatment measures.

Surgical Treatment
If treatment hasn't worked and you still have painful symptoms after a year, your GP may refer you to either an orthopaedic surgeon, a surgeon who specialises in surgery that involves bones, muscles and joints, a podiatric surgeon, a podiatrist who specialises in foot surgery. Surgery is sometimes recommended for professional athletes and other sportspeople whose heel pain is adversely affecting their career. Plantar release surgery. Plantar release surgery is the most widely used type of surgery for heel pain. The surgeon will cut the fascia to release it from your heel bone and reduce the tension in your plantar fascia. This should reduce any inflammation and relieve your painful symptoms. Surgery can be performed either as, open surgery, where the section of the plantar fascia is released by making a cut into your heel, endoscopic or minimal incision surgery - where a smaller incision is made and special instruments are inserted through the incision to gain access to the plantar fascia. Endoscopic or minimal incision surgery has a quicker recovery time, so you will be able to walk normally much sooner (almost immediately), compared with two to three weeks for open surgery. A disadvantage of endoscopic surgery is that it requires both a specially trained surgical team and specialised equipment, so you may have to wait longer for treatment than if you were to choose open surgery. Endoscopic surgery also carries a higher risk of damaging nearby nerves, which could result in symptoms such as numbness, tingling or some loss of movement in your foot. As with all surgery, plantar release carries the risk of causing complications such as infection, nerve damage and a worsening of your symptoms after surgery (although this is rare). You should discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both techniques with your surgical team. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (EST) is a fairly new type of non-invasive treatment. Non-invasive means it does not involve making cuts into your body. EST involves using a device to deliver high-energy soundwaves into your heel. The soundwaves can sometimes cause pain, so a local anaesthetic may be used to numb your heel. It is claimed that EST works in two ways. It is thought to, have a "numbing" effect on the nerves that transmit pain signals to your brain, help stimulate and speed up the healing process. However, these claims have not yet been definitively proven. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued guidance about the use of EST for treating plantar fasciitis. NICE states there are no concerns over the safety of EST, but there are uncertainties about how effective the procedure is for treating heel pain. Some studies have reported that EST is more effective than surgery and other non-surgical treatments, while other studies found the procedure to be no better than a placebo (sham treatment).
What Causes Plantar Fasciitis To Surface
Overview
Plantar Fasciitis is an inflammation caused by excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. The plantar fascia is a broad band of fibrous tissue which runs along the bottom surface of the foot, attaching at the bottom of the heel bone and extending to the forefoot. When the plantar fascia is excessively stretched, this can cause plantar fasciitis, which can also lead to heel pain, arch pain, and heel spurs.
Causes
Repeated small injuries to the fascia (with or without inflammation) are thought to be the cause of plantar fasciitis. The injury is usually near to where the plantar fascia attaches to your heel bone. You are more likely to injure your plantar fascia in certain situations. For example, if you are on your feet for a lot of the time, or if you do lots of walking, running, standing, etc, when you are not used to it. (Plantar fasciitis may be confused with 'Policeman's heel', but they are different. Policeman's heel is plantar calcaneal bursitis - inflammation of the sack of fluid (bursa) under the heel bone. This is not as common as plantar fasciitis.) Also, people with a sedentary lifestyle are more prone to plantar fasciitis. If you have recently started exercising on a different surface, for example, running on the road instead of a track. If you have been wearing shoes with poor cushioning or poor arch support. If you are overweight this will put extra strain on your heel. If there is overuse or sudden stretching of your sole. For example, athletes who increase running intensity or distance; poor technique starting 'off the blocks', etc. If you have a tight Achilles tendon (the big tendon at the bottom of your calf muscles above your heel). This can affect your ability to flex your ankle and make you more likely to damage your plantar fascia. Often there is no apparent cause for plantar fasciitis, particularly in older people. A common wrong belief is that the pain is due to a bony growth or 'spur' coming from the heel bone (calcaneum). Many people have a bony spur of the heel bone but not everyone with this gets plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
Pain is the main symptom. This can be anywhere on the underside of your heel. However, commonly, one spot is found as the main source of pain. This is often about 4 cm forward from your heel, and may be tender to touch. The pain is often worst when you take your first steps on getting up in the morning, or after long periods of rest where no weight is placed on your foot. Gentle exercise may ease things a little as the day goes by, but a long walk or being on your feet for a long time often makes the pain worse. Resting your foot usually eases the pain. Sudden stretching of the sole of your foot may make the pain worse, for example, walking up stairs or on tiptoes. You may limp because of pain. Some people have plantar fasciitis in both feet at the same time.
Diagnosis
X-rays are a commonly used diagnostic imaging technique to rule out the possibility of a bone spur as a cause of your heel pain. A bone spur, if it is present in this location, is probably not the cause of your pain, but it is evidence that your plantar fascia has been exerting excessive force on your heel bone. X-ray images can also help determine if you have arthritis or whether other, more rare problems, stress fractures, bone tumors-are contributing to your heel pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
To alleviate the stress and pain on the fascia, the person can take shorter steps and avoid walking barefoot. Activities that involve foot impact, such as jogging, should be avoided. The most effective treatments include the use of in-shoe heel and arch cushioning with calf-stretching exercises and night splints that stretch the calf and plantar fascia while the patient sleeps. Prefabricated or custom-made foot orthotics may also alleviate fascial tension and symptoms. Other treatments may include activity modifications, NSAIDs, weight loss in obese patients, cold and ice massage therapy, and occasional corticosteroid injections. However, because corticosteroid injections can predispose to plantar fasciosis, many clinicians limit these injections. For recalcitrant cases, physical therapy, oral corticosteroids, and cast immobilization should be used before surgical intervention is considered. A newer form of treatment for recalcitrant types of plantar fasciosis is extracorporeal pulse activation therapy (EPAT), in which low-frequency pulse waves are delivered locally using a handheld applicator. The pulsed pressure wave is a safe, noninvasive technique that stimulates metabolism and enhances blood circulation, which helps regenerate damaged tissue and accelerate healing. EPAT is being used at major medical centers.
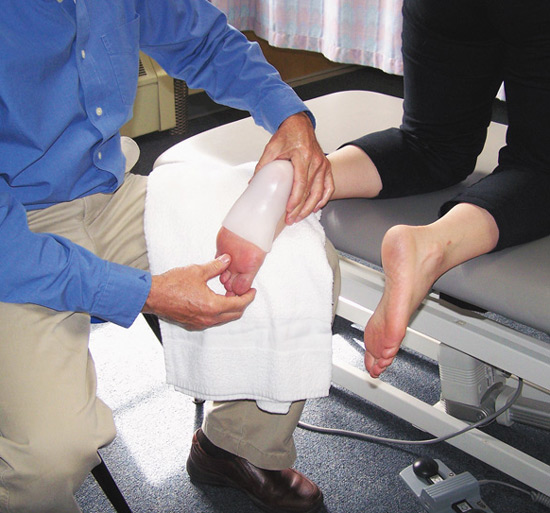
Surgical Treatment
Surgery should be reserved for patients who have made every effort to fully participate in conservative treatments, but continue to have pain from plantar fasciitis. Patients should fit the following criteria. Symptoms for at least 9 months of treatment. Participation in daily treatments (exercises, stretches, etc.). If you fit these criteria, then surgery may be an option in the treatment of your plantar fasciitis. Unfortunately, surgery for treatment of plantar fasciitis is not as predictable as a surgeon might like. For example, surgeons can reliably predict that patients with severe knee arthritis will do well after knee replacement surgery about 95% of the time. Those are very good results. Unfortunately, the same is not true of patients with plantar fasciitis.
Stretching Exercises
You may begin exercising the muscles of your foot right away by gently stretching them as follows. Prone hip extension, Lie on your stomach with your legs straight out behind you. Tighten up your buttocks muscles and lift one leg off the floor about 8 inches. Keep your knee straight. Hold for 5 seconds. Then lower your leg and relax. Do 3 sets of 10. Towel stretch, Sit on a hard surface with one leg stretched out in front of you. Loop a towel around your toes and the ball of your foot and pull the towel toward your body keeping your knee straight. Hold this position for 15 to 30 seconds then relax. Repeat 3 times. When the towel stretch becomes too easy, you may begin doing the standing calf stretch. Standing calf stretch, Facing a wall, put your hands against the wall at about eye level. Keep one leg back with the heel on the floor, and the other leg forward. Turn your back foot slightly inward (as if you were pigeon-toed) as you slowly lean into the wall until you feel a stretch in the back of your calf. Hold for 15 to 30 seconds. Repeat 3 times. Do this exercise several times each day. Sitting plantar fascia stretch, Sit in a chair and cross one foot over your other knee. Grab the base of your toes and pull them back toward your leg until you feel a comfortable stretch. Hold 15 seconds and repeat 3 times. When you can stand comfortably on your injured foot, you can begin standing to stretch the bottom of your foot using the plantar fascia stretch. Achilles stretch, Stand with the ball of one foot on a stair. Reach for the bottom step with your heel until you feel a stretch in the arch of your foot. Hold this position for 15 to 30 seconds and then relax. Repeat 3 times. After you have stretched the bottom muscles of your foot, you can begin strengthening the top muscles of your foot. Frozen can roll, Roll your bare injured foot back and forth from your heel to your mid-arch over a frozen juice can. Repeat for 3 to 5 minutes. This exercise is particularly helpful if done first thing in the morning. Towel pickup, With your heel on the ground, pick up a towel with your toes. Release. Repeat 10 to 20 times. When this gets easy, add more resistance by placing a book or small weight on the towel. Balance and reach exercises, Stand upright next to a chair. This will provide you with balance if needed. Stand on the foot farthest from the chair. Try to raise the arch of your foot while keeping your toes on the floor. Keep your foot in this position and reach forward in front of you with your hand farthest away from the chair, allowing your knee to bend. Repeat this 10 times while maintaining the arch height. This exercise can be made more difficult by reaching farther in front of you. Do 2 sets. Stand in the same position as above. While maintaining your arch height, reach the hand farthest away from the chair across your body toward the chair. The farther you reach, the more challenging the exercise. Do 2 sets of 10. Heel raise, Balance yourself while standing behind a chair or counter. Using the chair to help you, raise your body up onto your toes and hold for 5 seconds. Then slowly lower yourself down without holding onto the chair. Hold onto the chair or counter if you need to. When this exercise becomes less painful, try lowering on one leg only. Repeat 10 times. Do 3 sets of 10. Side-lying leg lift, Lying on your side, tighten the front thigh muscles on your top leg and lift that leg 8 to 10 inches away from the other leg. Keep the leg straight. Do 3 sets of 10.
Symptoms Of Joint Pain in the Foot
Metatarsal pain, often referred to as metatarsalgia, can be caused by several foot conditions, including Freiberg's disease, Morton's neuroma and sesamoiditis. According to a 2003 article in the British Journal of Sports Plantar Fasciitis Medicine,” a flat or high arch is one of many risk factors for lower extremity injuries including foot injuries. Poor circulation occurs when there is not enough blood supplied to an area to meet the needs of the cells.
U-Shaped portion surrounds sore callus and reduces pain by transferring pressure from callus to the cushion. Soft orthotics cushion the ball and arches of the feet and protect them from injury and pain, while rigid orthotics correct abnormal foot angles and movements that can cause or worsen pain in the ball of the foot. Many insoles fit inside of slippers so that people suffering from pain in the ball of the foot can walk more comfortably inside their homes as well as outside. In addition, some insoles include added deodorizers to help decrease foot odor. While gel or foam insoles are sold at pharmacies, grocery stores and sporting-goods stores, orthotics require a visit to a podiatrist, who will make a cast of the foot and build a custom-fit insole from the cast. Foam, gel and soft orthotics require replacement once a year or more as the cushioning wears out. Rigid orthotics rarely need replacement. Hip bone spur can cause a lot of discomfort.
Those affected by inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and Achilles tendonitis are also likely to experience pain and swelling in the ankles. If the joints in the feet get affected by osteoarthritis, it gives rise to pain, stiffness, swelling in or around the joint, and restricted range of motion. Since pain in the feet could be caused due to a variety of reasons, the treatment will depend on the underlying cause. Many a time, pain could be experienced by people who perform high-impact exercises such as running, jogging and other sports. Those who have been experiencing pain while running must make sure that they wear a good quality footwear. Painkillers or steroids might be prescribed for the treatment of a sprained ankle.
Another solution is to wear custom foot orthotics, like ezWalker ® Performance Custom Orthotics, in your shoes to help correct your body posture, stabilize your balance, relieve pain during follow-through and evenly redistribute your weight on your feet. EzWalker® Custom Orthotics are specifically made for each of your feet to properly support your arches while reducing pressure on the balls of your feet. With ezWalker® Custom Orthotics, you'll walk from lateral heel to medial forefoot for better biomechanics of your entire body. This condition manifests as a skin lesion that assumes a ring-like pattern. It can affect any region of the body, right from the scalp to the foot. One such common home remedy is the use of bleach. Many people claim that this is a very effective ringworm treatment.
During the average lifetime our feet cover over 70,000 miles, the equivalent of walking four times around the world., so it's not surprising that problems can occur. Indeed around three-quarters of all adults will experience some sort of problem with their feet at some time. And without treatment most foot complaints will become gradually worse with time. This means people often endure painful conditions for far too long, and the problem can get worse. People often assume nothing can be done to help their condition, but in fact these conditions are extremely treatable. Swollen lump on big toe joint; lump may become numb but also make walking painful.
U-Shaped portion surrounds sore callus and reduces pain by transferring pressure from callus to the cushion. Soft orthotics cushion the ball and arches of the feet and protect them from injury and pain, while rigid orthotics correct abnormal foot angles and movements that can cause or worsen pain in the ball of the foot. Many insoles fit inside of slippers so that people suffering from pain in the ball of the foot can walk more comfortably inside their homes as well as outside. In addition, some insoles include added deodorizers to help decrease foot odor. While gel or foam insoles are sold at pharmacies, grocery stores and sporting-goods stores, orthotics require a visit to a podiatrist, who will make a cast of the foot and build a custom-fit insole from the cast. Foam, gel and soft orthotics require replacement once a year or more as the cushioning wears out. Rigid orthotics rarely need replacement. Hip bone spur can cause a lot of discomfort.
Those affected by inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and Achilles tendonitis are also likely to experience pain and swelling in the ankles. If the joints in the feet get affected by osteoarthritis, it gives rise to pain, stiffness, swelling in or around the joint, and restricted range of motion. Since pain in the feet could be caused due to a variety of reasons, the treatment will depend on the underlying cause. Many a time, pain could be experienced by people who perform high-impact exercises such as running, jogging and other sports. Those who have been experiencing pain while running must make sure that they wear a good quality footwear. Painkillers or steroids might be prescribed for the treatment of a sprained ankle.

Another solution is to wear custom foot orthotics, like ezWalker ® Performance Custom Orthotics, in your shoes to help correct your body posture, stabilize your balance, relieve pain during follow-through and evenly redistribute your weight on your feet. EzWalker® Custom Orthotics are specifically made for each of your feet to properly support your arches while reducing pressure on the balls of your feet. With ezWalker® Custom Orthotics, you'll walk from lateral heel to medial forefoot for better biomechanics of your entire body. This condition manifests as a skin lesion that assumes a ring-like pattern. It can affect any region of the body, right from the scalp to the foot. One such common home remedy is the use of bleach. Many people claim that this is a very effective ringworm treatment.

During the average lifetime our feet cover over 70,000 miles, the equivalent of walking four times around the world., so it's not surprising that problems can occur. Indeed around three-quarters of all adults will experience some sort of problem with their feet at some time. And without treatment most foot complaints will become gradually worse with time. This means people often endure painful conditions for far too long, and the problem can get worse. People often assume nothing can be done to help their condition, but in fact these conditions are extremely treatable. Swollen lump on big toe joint; lump may become numb but also make walking painful.
All About Achilles Tendonitis
Overview
 Achilles-tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the Achilles tendon (back of the ankle). This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf muscles from the leg and knee to the heel. This structure is important in standing on your toes or in the pushing-off phase of walking, running, or jumping.Achilles-tendinitis is usually a grade 1 or 2 strain of the tendon. A grade 1 strain is a mild strain. There is a slight pull of the tendon without obvious tendon tearing. (There is microscopic tendon tearing.) There is no loss of strength, and the tendon is the correct length. A grade 2 strain is a moderate strain. There is tearing of tendon fibers within the substance of the tendon or where the tendon attaches to muscle or bone. The length of the tendon or whole muscle-tendon-bone unit is increased, and there is usually decreased strength. A grade 3 strain is a complete rupture of the tendon.
Achilles-tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the Achilles tendon (back of the ankle). This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf muscles from the leg and knee to the heel. This structure is important in standing on your toes or in the pushing-off phase of walking, running, or jumping.Achilles-tendinitis is usually a grade 1 or 2 strain of the tendon. A grade 1 strain is a mild strain. There is a slight pull of the tendon without obvious tendon tearing. (There is microscopic tendon tearing.) There is no loss of strength, and the tendon is the correct length. A grade 2 strain is a moderate strain. There is tearing of tendon fibers within the substance of the tendon or where the tendon attaches to muscle or bone. The length of the tendon or whole muscle-tendon-bone unit is increased, and there is usually decreased strength. A grade 3 strain is a complete rupture of the tendon.
Causes
Tight or fatigued calf muscles, which transfer the burden of running to the Achilles. This can be due to poor stretching, rapidly increasing distance, or over-training excessive hill running or speed work, both of which stress the Achilles more than other types of running. Inflexible running shoes, which, in some cases, may force the Achilles to twist. Runners who overpronate (feet rotate too far inward on impact) are most susceptible to Achilles tendinitis.
Symptoms
The pain associated with Achilles tendonitis can come on gradually or be caused by some type of leg or foot trauma. The pain can be a shooting, burning, or a dull ache. You can experience the pain at either the insertion point on the back of the heel or upwards on the Achilles tendon within a few inches. Swelling is also common along the area with the pain. The onset of discomfort at the insertion can cause a bump to occur called a Haglund's deformities or Pump bump. This can be inflammation in the bursa sac that surrounds the insertion of the Achilles tendon, scar tissue from continuous tares of the tendon, or even some calcium buildup. In this situation the wearing of closed back shoes could irritate the bump. In the event of a rupture, which is rare, the foot will not be able to go through the final stage of push off causing instability. Finally, you may experience discomfort, even cramping in the calf muscle.
Diagnosis
During an examination of the foot and ankle, you doctor will look for the following signs, Achilles tendon swelling or thickening. Bone spurs appearing at the lower part of the tendon at the back of the hell. Pain at the middle or lower area of the Achilles tendon. Limited range of motion of the foot and ankle, and a decreased ability to flex the foot. Your doctor may perform imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendinitis. X-rays show images of the bones and can help the physician to determine if the Achilles tendon has become hardened, which indicated insertional Achilles tendinitis. MRI scans may not be necessary, but they are important guides if you are recommended to have surgical treatment. An MRI can show the severity of the damage and determine what kind of procedure would be best to address the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Take a course (5 - 7 days) of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs(ibuprofen/voltaren/cataflam/mobic) available from your general practitioner or pharmacist. Apply ice to the Achilles - for 10 minutes every 2 hours, in order to reduce the inflammation. Avoid weight-bearing activities and keep foot elevated where possible. Self-massage - using arnica oil or anti-inflammatory gel. Rub in semi-circles in all directions away from the knotted tissue, three times a day once the nodule is gone, stretch the calf muscle gently do not start running until you can do heel raises and jumping exercises without pain return to running gradually full recovery is usually between six to eight weeks.

Surgical Treatment
Your doctor may recommend surgery if, after around six months, other treatments haven?t worked and your symptoms are having an impact on your day-to-day life. Surgery involves removing damaged areas of your tendon and repairing them.
Prevention
While it may not be possible to prevent Achilles tendinitis, you can take measures to reduce your risk. Increase your activity level gradually. If you're just beginning an exercise regimen, start slowly and gradually increase the duration and intensity of the training. Take it easy. Avoid activities that place excessive stress on your tendons, such as hill running. If you participate in a strenuous activity, warm up first by exercising at a slower pace. If you notice pain during a particular exercise, stop and rest. Choose your shoes carefully. The shoes you wear while exercising should provide adequate cushioning for your heel and should have a firm arch support to help reduce the tension in the Achilles tendon. Replace your worn-out shoes. If your shoes are in good condition but don't support your feet, try arch supports in both shoes. Stretch daily. Take the time to stretch your calf muscles and Achilles tendon in the morning, before exercise and after exercise to maintain flexibility. This is especially important to avoid a recurrence of Achilles tendinitis. Strengthen your calf muscles. Strong calf muscles enable the calf and Achilles tendon to better handle the stresses they encounter with activity and exercise. Cross-train. Alternate high-impact activities, such as running and jumping, with low-impact activities, such as cycling and swimming.
 Achilles-tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the Achilles tendon (back of the ankle). This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf muscles from the leg and knee to the heel. This structure is important in standing on your toes or in the pushing-off phase of walking, running, or jumping.Achilles-tendinitis is usually a grade 1 or 2 strain of the tendon. A grade 1 strain is a mild strain. There is a slight pull of the tendon without obvious tendon tearing. (There is microscopic tendon tearing.) There is no loss of strength, and the tendon is the correct length. A grade 2 strain is a moderate strain. There is tearing of tendon fibers within the substance of the tendon or where the tendon attaches to muscle or bone. The length of the tendon or whole muscle-tendon-bone unit is increased, and there is usually decreased strength. A grade 3 strain is a complete rupture of the tendon.
Achilles-tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the Achilles tendon (back of the ankle). This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf muscles from the leg and knee to the heel. This structure is important in standing on your toes or in the pushing-off phase of walking, running, or jumping.Achilles-tendinitis is usually a grade 1 or 2 strain of the tendon. A grade 1 strain is a mild strain. There is a slight pull of the tendon without obvious tendon tearing. (There is microscopic tendon tearing.) There is no loss of strength, and the tendon is the correct length. A grade 2 strain is a moderate strain. There is tearing of tendon fibers within the substance of the tendon or where the tendon attaches to muscle or bone. The length of the tendon or whole muscle-tendon-bone unit is increased, and there is usually decreased strength. A grade 3 strain is a complete rupture of the tendon.
Causes
Tight or fatigued calf muscles, which transfer the burden of running to the Achilles. This can be due to poor stretching, rapidly increasing distance, or over-training excessive hill running or speed work, both of which stress the Achilles more than other types of running. Inflexible running shoes, which, in some cases, may force the Achilles to twist. Runners who overpronate (feet rotate too far inward on impact) are most susceptible to Achilles tendinitis.
Symptoms
The pain associated with Achilles tendonitis can come on gradually or be caused by some type of leg or foot trauma. The pain can be a shooting, burning, or a dull ache. You can experience the pain at either the insertion point on the back of the heel or upwards on the Achilles tendon within a few inches. Swelling is also common along the area with the pain. The onset of discomfort at the insertion can cause a bump to occur called a Haglund's deformities or Pump bump. This can be inflammation in the bursa sac that surrounds the insertion of the Achilles tendon, scar tissue from continuous tares of the tendon, or even some calcium buildup. In this situation the wearing of closed back shoes could irritate the bump. In the event of a rupture, which is rare, the foot will not be able to go through the final stage of push off causing instability. Finally, you may experience discomfort, even cramping in the calf muscle.
Diagnosis
During an examination of the foot and ankle, you doctor will look for the following signs, Achilles tendon swelling or thickening. Bone spurs appearing at the lower part of the tendon at the back of the hell. Pain at the middle or lower area of the Achilles tendon. Limited range of motion of the foot and ankle, and a decreased ability to flex the foot. Your doctor may perform imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendinitis. X-rays show images of the bones and can help the physician to determine if the Achilles tendon has become hardened, which indicated insertional Achilles tendinitis. MRI scans may not be necessary, but they are important guides if you are recommended to have surgical treatment. An MRI can show the severity of the damage and determine what kind of procedure would be best to address the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Take a course (5 - 7 days) of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs(ibuprofen/voltaren/cataflam/mobic) available from your general practitioner or pharmacist. Apply ice to the Achilles - for 10 minutes every 2 hours, in order to reduce the inflammation. Avoid weight-bearing activities and keep foot elevated where possible. Self-massage - using arnica oil or anti-inflammatory gel. Rub in semi-circles in all directions away from the knotted tissue, three times a day once the nodule is gone, stretch the calf muscle gently do not start running until you can do heel raises and jumping exercises without pain return to running gradually full recovery is usually between six to eight weeks.

Surgical Treatment
Your doctor may recommend surgery if, after around six months, other treatments haven?t worked and your symptoms are having an impact on your day-to-day life. Surgery involves removing damaged areas of your tendon and repairing them.
Prevention
While it may not be possible to prevent Achilles tendinitis, you can take measures to reduce your risk. Increase your activity level gradually. If you're just beginning an exercise regimen, start slowly and gradually increase the duration and intensity of the training. Take it easy. Avoid activities that place excessive stress on your tendons, such as hill running. If you participate in a strenuous activity, warm up first by exercising at a slower pace. If you notice pain during a particular exercise, stop and rest. Choose your shoes carefully. The shoes you wear while exercising should provide adequate cushioning for your heel and should have a firm arch support to help reduce the tension in the Achilles tendon. Replace your worn-out shoes. If your shoes are in good condition but don't support your feet, try arch supports in both shoes. Stretch daily. Take the time to stretch your calf muscles and Achilles tendon in the morning, before exercise and after exercise to maintain flexibility. This is especially important to avoid a recurrence of Achilles tendinitis. Strengthen your calf muscles. Strong calf muscles enable the calf and Achilles tendon to better handle the stresses they encounter with activity and exercise. Cross-train. Alternate high-impact activities, such as running and jumping, with low-impact activities, such as cycling and swimming.